44 nucleotides label
Answered: NUCLEOTIDES Label the parts of these… | bartleby ISBN: 9780134580999. Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn. Publisher: PEARSON. expand_less. 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 2 Chemistry Comes Alive 3 Cells: The Living Units 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric 5 The Integumentary System 6 Bones And Skeletal Tissues 7 The Skeleton 8 Joints 9 Muscles And Muscle Tissue 10 The Muscular System 11 ... Home - Nucleotide - NCBI Nucleotide The Nucleotide database is a collection of sequences from several sources, including GenBank, RefSeq, TPA and PDB. Genome, gene and transcript sequence data provide the foundation for biomedical research and discovery. Using Nucleotide Quick Start Guide FAQ Help GenBank FTP RefSeq FTP Nucleotide Tools Submit to GenBank LinkOut
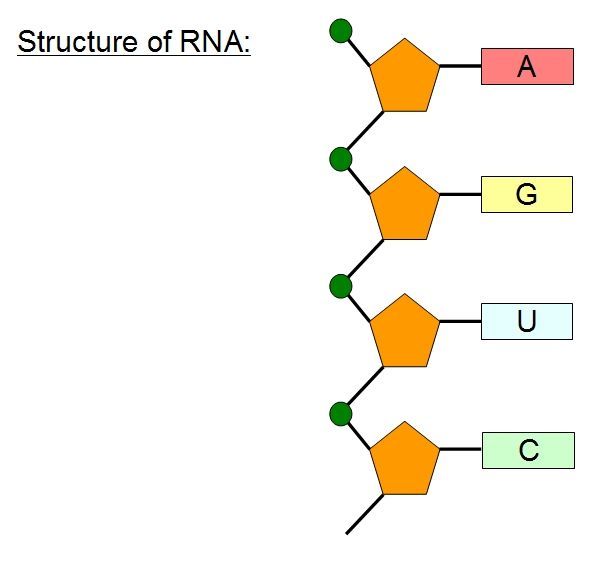
Nucleotide - Genome.gov A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).

Nucleotides label
Nucleosides and Nucleotides - Sigma-Aldrich Nucleosides are glycosylamines obtained by chemical or enzymatic decomposition of nucleic acids and contain two components: a five-carbon sugar ( ribose or 2' deoxyribose) and a nitrogen base. The nitrogenous bases are planar, aromatic, heterocyclic molecules. For the most part, are derivatives of purine or pyrimidine. Nucleotide - Wikipedia In experimental biochemistry, nucleotides can be radiolabeled using radionuclides to yield radionucleotides. 5-nucleotides are also used in flavour enhancers as food additive to enhance the umami taste, often in the form of a yeast extract. Contents 1 Structure 2 Synthesis 2.1 Pyrimidine ribonucleotide synthesis 2.2 Purine ribonucleotide synthesis The 5 Kinds of Nucleotides - ThoughtCo The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U, respectively. The name of the base is generally used as the name of the nucleotide, although this is technically incorrect. The bases combine with the sugar to make the nucleotides adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, and uridine.
Nucleotides label. Solved Ch.4 Nucleic Acids A. Nucleotides 1. Label the figure - Chegg 100% (2 ratings) 2. DNA strands exhibit polarity i.e. both the ends are different. These ends are designated as 5' …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Ch.4 Nucleic Acids A. Nucleotides 1. Label the figure to the right with the names of each of the three components of a nucleotide. 2 is the nucleotide to the right a DNA nucleotide ... Nucleotides in DNA | Science Primer Nucleotide Nucleoside. DNA is a nucleotide polymer, or polynucleotide. Each nucleotide contains three components: A five carbon sugar. A phosphate molecule. A nitrogen-containing base. The sugar carbon atoms are numbered 1 to 5. The nitrogenous base attaches to base 1, and the phosphate group attaches to base 5. Nucleotides labeled with... - Jena Bioscience Nucleotides labeled with... Biotin Adenosines Guanosines Uridines Cytidines Desthiobiotin Digoxigenin DNP (Dinitrophenol) Photo-labile groups ("Caged") Adenosines Guanosines Xanthosines Triple bonds (Alkyne) DBCO Azide (-N 3) Adenosines Guanosines Uridines Cytidines Thymidines TCO Vinyl Free amino group (-NH 2) Adenosines Guanosines Cytidines DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides labeled nucleotides may be incorporated by a variety of methods including in vitro transcription with sp6, t3 or t7 rna polymerase, 3' end labeling with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (tdt), t4 dna polymerase or t7 dna polymerase, random primed dna labeling with klenow fragment, cdna labeling with amv or m-mulv reverse transcriptase, nick …
Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification Nucleotides are the biological molecules that serve as the building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They are essential for all the functions performed by a living cell. Not only this, but they are also essential for transferring information to new cells or the next generation of the living organisms. What are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io Figure 2: The chemical assembly of the three parts of the nucleotide, the phosphate (blue box), nitrogenous base (red box) and the pentose sugar. This particular nucleotide is adenine. The assembly of nucleotides (1) differentiates them from nucleosides, which do not contain a phosphate group (in the blue box); (2) allows the nucleotide to ... Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Sketch And Label A Nucleotide : Solved Problem 1 What Are The Three ... Creating your own labels is easy. A bond between nucleotides in rna and dna molecules. Using arrows and brackets, identify and label at least one example of each of the following. 3.3.5 draw and label a simple diagram of the molecular structure of dna.here i demonstrate drawing the structure of dna. The above structure is a nucleotide.
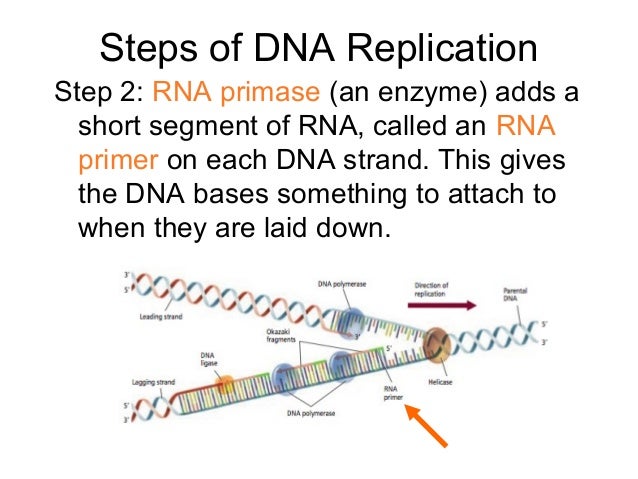
Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Nucleic acid probes can be labeled with tags or other modifications during synthesis. However, purchasing custom oligonucleotide probes (especially RNA) can be quite expensive depending on the modification and whether costly purification services are required. 9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition Now let's consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base ( Figure 9.3 ). There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA. How (and Why) to Label Nucleic Acids - Bitesize Bio Nucleic acids can be labeled at their 5´ end, 3´ end, or throughout the molecule depending on the particular application, including: to generate information on gene integrity and copy number (blot) to diagnose specific sequences and chromosomal aberrations (in situ hybridization) Numbering convention for nucleotides - Bio-Synthesis, Inc. Figure 1 shows the general structure of nucleotides illustrating the numbering convention for the pentose ring. The ribose structure is shown in the Haworth projection. Phosphate groups join the nucleic acid monomers together in a linear manner. Phosphate groups are attached to the 3' and 5' positions of the ribose sugars.
Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram | Science Trends Nucleotides are molecules which serve as the building blocks, or monomer units, for the creation of important polymers like ribonucleic acid or RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. As mentioned, nucleotides have three component parts: a five-sided carbon sugar, a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group.
Labeled Nucleotides - Biotium Biotin-11-dUTP, 1 mM Solution. From: $253 Sizes: 50 uL Catalog #: 40029. Biotin-11-dUTP, 1 mM Solution. Biotin-11-dUTP can be enzymatically incorporated into DNA via nick translation, random priming, or 3′-end terminal labeling. The number '11' is the number of atoms in the linker between biotin and dUTP.
Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 the labeled aha-dutp and aha-dctp nucleotides can be used to generate labeled nucleic acid hybridization probes for many molecular biology and molecular cytogenetics applications, including two-color microarray assays, northern and southern blots, colony and plaque hybridizations, dna sequencing, primer extension, dna and rna amplification and …
Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS A nucleotide is an organic molecule with a basic composition of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate. DNA and RNA are polynucleotides, which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases. Nucleotides are essential for carrying out metabolic and physiological activities.
Digoxigenin (DIG) Labeling Methods - Sigma-Aldrich Digoxigenin (DIG) Labeling and Anti-DIG Antibody. The DIG System is the nonradioactive technology of choice to label and detect nucleic acids for multiple applications. The system is based on a steroid isolated from digitalis plants (Digitalis purpurea and Digitalis lanata). These plants are the only natural source of digoxigenin, so the anti ...
Fluorescent and Hapten Labeled Nucleotides | PerkinElmer Labeled nucleotides are critical elements for sequence detection in a wide variety of techniques including in situ hybridization, microarrays and DNA sequencing. Our fluorescent and hapten labeled nucleotides provide a reliable, sensitive alternative to working with radioactivity through both direct and indirect detection methods.
Purines, Pyrimidines, and Nucleotides - Bio-Syn A nucleotide is made up of three units: A nitrogen-containing base, A five-carbon sugar, One, two or three phosphate groups. There are five common bases. Two of these bases are derivatives of purine. These are adenine and guanine. Three of the bases are pyrimidine derivatives. These are cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected Nucleotides are the building blocks of the DNA and RNA used as genetic material. Nucleotides also are used for cell signaling and to transport energy throughout cells. You may be asked to name the three parts of a nucleotide and explain how they are connected or bonded to each other. Here's the answer for both DNA and RNA .
The Structure of DNA A phosphate group (a phosphorous atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms.) (Labeled P) And one of four nitrogen-containing molecules called nucleotides . (Labeled A, T, C, or G) Alternating sugar and phosphate units form the two sides of a ladder-shaped arrangement with the rungs or steps each formed by a pair of nucleotide bases.



Post a Comment for "44 nucleotides label"