40 under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?
Underwhatcircumstancesdoesadeviantlabelleadfromprimary - Course Hero Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is internalized d. when the deviant label is applied later in life e. when the deviant label concerns a ... Why Women Should Make the Abortion Decision: Damned If You … However, “twenty state Medicaid programs do not fund abortion under any circumstances.” As mentioned above, the Hyde Amendment prohibits state Medicaid programs to use federal funds to help pay for abortions. This barrier contributes to a lack of funding, which in turn hurts poor women who are desperately searching for a way to pay for the procedure (Boston Women’s …
under what circumstances will a judge grant a motion for a ... - Pyranic Mention three circumstances in which the office of the Judge of the Supreme Court falls vacant. ... In the following sentence elaborate the parts given in bold. Under the circumstances it was a very unfortunate remark for the bird to make. by tony# ... under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? by Get ...
Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?
Sociology Exam 2 Flashcards | Quizlet Under what circumstances does a deviant label transition from primary to secondary deviance? a.when the deviant label is internalized b.when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people c.when the deviant label is applied later in life d.when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful a.when the deviant label is internalized Putting Case Studies to Work: Applications to Development Practice ... The Case for Case Studies - May 2022 Secondary Deviance: Definition & Examples - Study.com Primary deviance is a deviant act that receives little social reaction or mild, corrective reaction. It's important to remember that not all deviant acts produce long-term negative outcomes. Some...
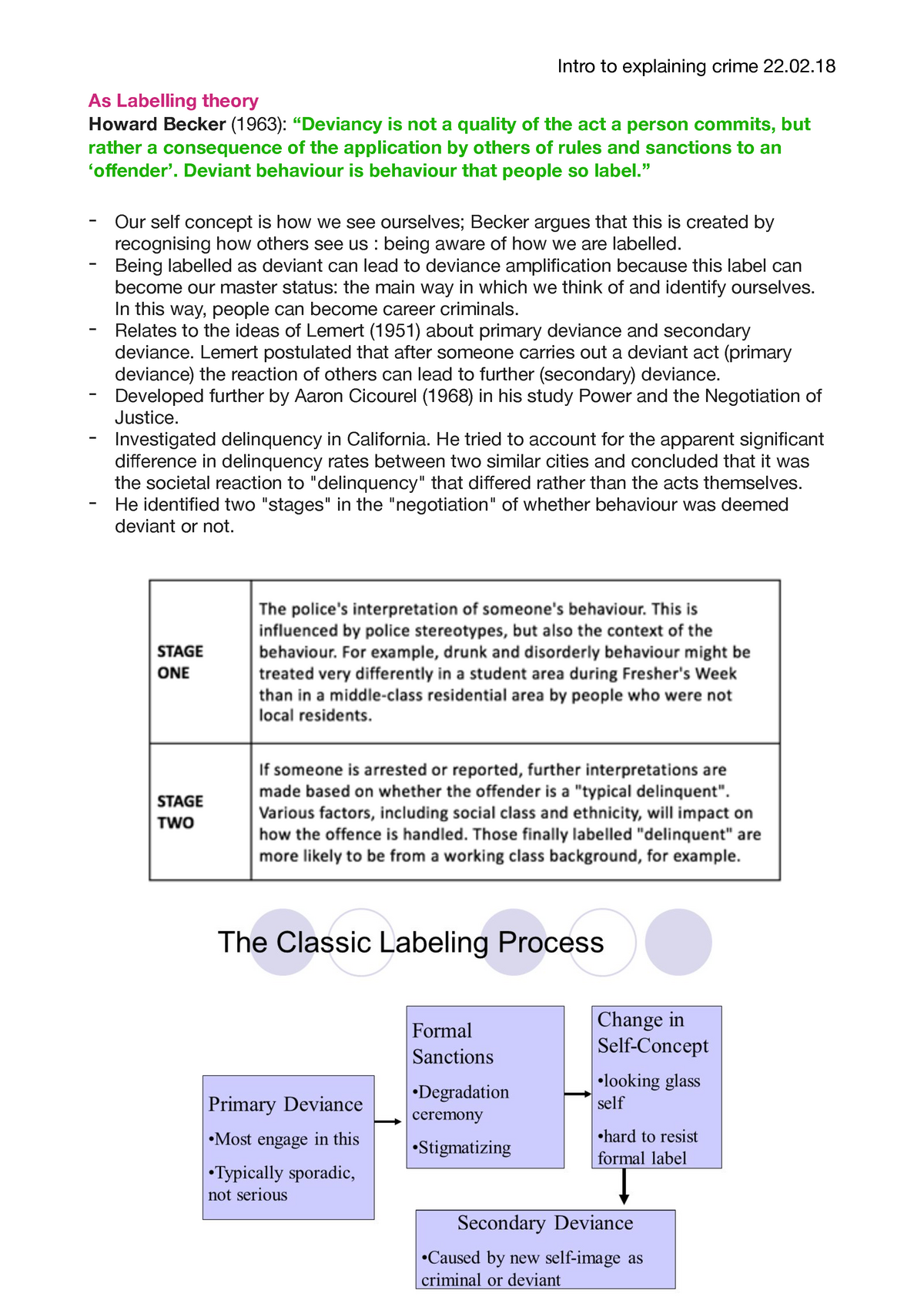
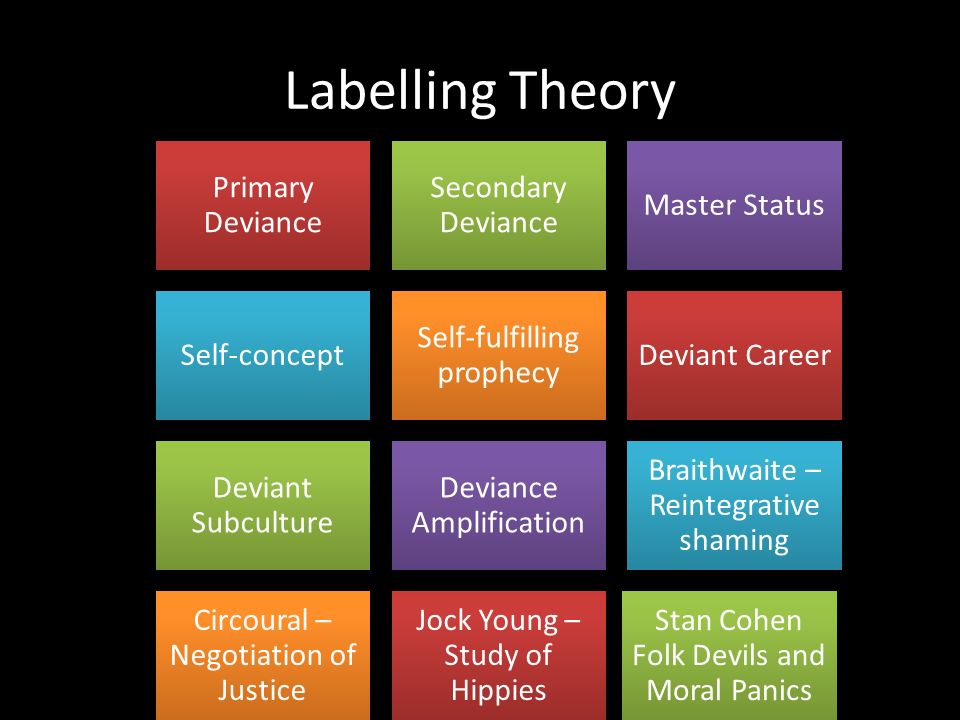
Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?. Labelling Theory of Crime - A Summary - ReviseSociology Labelling has real consequences - it can lead to deviancy amplification, the self-fulfilling prophecy and deviant careers. Lemert - primary and secondary deviance. Becker - labelling, the deviant career and the master status . Labelling theory applied to education - the self-fulfilling prophecy. Moral panics, folk devils and deviancy ... Chapter 7. Deviance, Crime, and Social Control - Introduction to ... Deviance and Control. Deviance is a violation of norms. Whether or not something is deviant depends on contextual definitions, the situation, and people's response to the behaviour. Society seeks to limit deviance through the use of sanctions that help maintain a system of social control. Difference Between Primary and Secondary Deviance In primary deviance, the person commits a deviant action without knowing that h/she is going against the norm system. However, in secondary deviance, the person is already labeled as a deviant but still h/she continues to engage in that particular act. Now, we will look at these two terms, primary deviance and secondary deviance, in detail. Sociology 200 Chapter 6 Flashcards | Quizlet Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? when the deviant label is accepted as part of one's identity Deviance occurs in all cultures and is impossible to completely get rid of in society. True
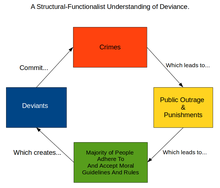
Sociology Quiz #3 Flashcards | Quizlet a. the absolute distinction between primary and secondary groups b. the goal-orientated nature of primary groups c. the way that primary groups can lead to membership in secondary groups d. the way that secondary groups can lead to close personal ties of primary groups e. the relative distinction between primary and secondary groups Deviant Social Behaviors that have become Acceptable Behavior considered deviant today may be socially acceptable after another generation or two, and normal within another generation after that. This has certainly been true over the course of the twentieth century, and may be no less true in the twenty-first. At the turn of the twentieth century, premarital sex was considered deviant. According to sociologists, how is deviance relative? Deviance defines moral boundaries, people learn right from wrong by defining people as deviant. A serious form of deviance forces people to come together and react in the same way against it. Deviance pushes society's moral boundaries which, in turn leads to social change. When social deviance is committed, the collective conscience is offended. Chapter 1. An Introduction to Sociology - Introduction to Sociology ... From this point of view, deviance is not a quality of the act the person commits, but rather a consequence of the application by other of rules and sanctions to an "offender." The deviant is one to whom that label has been successfully applied; deviant behavior is behaviour that people so label (1963).
Labeling Theory of Deviance: Definition & Examples Secondary deviance, on the other hand, refers to acts that are labeled by the society as deviant and attached to one's identity thus affecting one's self-concept. What is labeled as deviant depends on the legal forces of the society and the law that the society entails, thus what is labeled as deviant will differ from society to society? About The Real World_ an Introduction to Sociology ( PDFDrive ) - Scribd Chapter 8 (Race and Ethnicity as Lived Experi-Chapter 6 (Deviance): A new chapter opener uses mar- ence): The chapter opener has been updated with more ijuana, and our views regarding marijuana use, to illus- current data on the proportion of Americans who identify trate how cultural values, including what we consider to be as mixed race and also highlights the plan by the … Organizational Behavior By Stephen P Robbins Timothy A Judge … Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. 18. Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to ... answered 18. Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is internalized d. when the deviant label is applied later in life
Theories of Crime and Deviance | Boundless Sociology | | Course Hero Labeling theory refers to the idea that individuals become deviant when a deviant label is applied to them; they adopt the label by exhibiting the behaviors, actions, and attitudes associated with the label. Labeling theory argues that people become deviant as a result of others forcing that identity upon them.
Media Theorists, ideas & arguments | alevelmedia Referred to as the 'ideology of protection' model. (Deviant Youth, 1995). 'Normal' adult and youth behaviour, contrasted with deviant youth behaviour, allows the state to have more control. Young people need constant surveillance and monitoring. Chris Allen – studied the representation Muslims in the media.
Evaluacija edukacije i indirektnog kontakta kao strategija promene ... Evaluacija edukacije i indirektnog kontakta kao strategija promene stavova prema osobama sa psihijatrijskom dijagnozom
Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead - Course Hero 49. Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applied by a large number of peopleb. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is accepted by the individuald. when the deviant label is applied later in life ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy ...
under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to ... Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? a. when the deviant label is applies by a large number of people to that individual b. when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful c. when the deviant label is accepted by the individual and seen as deviant
The theory that society creates deviance by identifying particular ... As such, labeling theory suggests that deviance is caused by the deviant's being labeled as morally inferior, the deviant's internalizing the label and finally the deviant's acting according to that specific label (i.e., an individual labelled as "deviant" will act accordingly).
Deviance | Boundless Sociology | | Course Hero deviance: Actions or behaviors that violate formal and informal cultural norms, such as laws or the norm that discourages public nose-picking. Informal Deviance: Deviance, in a sociological context, describes actions or behaviors that violate social norms, including formally-enacted rules (e.g., crime), as well as informal violations of social ...
Sociology: Exam #2 Flashcards | Quizlet Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? when there are social or legal sanctions and the deviant label is internalized _____ work is the dominant form of employment in the postindustrial economy. Service
Chapter 4 -- Risk Factors for Youth Violence - NCBI Bookshelf Research has documented the magnitude of youth violence and the trends in that violence over time. But what do we know about why young people become involved in violence? Why do some youths get caught up in violence while others do not? There is no simple answer to these questions, but scientists have identified a number of things that put children and adolescents …
Because of ________, deviance is often seen as mental sickness rather ... Secondary deviance describes a situation in which a person has been publicly identified as deviant, such as by being classified as mentally unstable or criminal. Labeling theory emphasizes that being labeled can generate a self-fulfilling prophecy whereby others behave toward the labeled person in ways that confirm or reinforce the label.
The risk need responsivity model of offender rehabilitation: Is … The current paper critically reviews the Risk-Need-Responsivity (RNR) and Good Lives Model (GLM) approaches to correctional treatment. Research, or the lack thereof, is discussed in terms of whether there is a need for a new model of offender rehabilitation. We argue that although there is a wealth of research in support of RNR approaches, there is presently very little available research ...
Access Denied - LiveJournal Hier sollte eine Beschreibung angezeigt werden, diese Seite lässt dies jedoch nicht zu.
Success Essays - Assisting students with assignments online Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply.
Sociology of Deviant Behavior Notes - SociologyofDeviantBehaviorNotes ... View Notes - Sociology of Deviant Behavior Notes from SOCIOLOGY 4610 at Ohio State University. SociologyofDeviantBehaviorNotes low moderate and high deviant behaviors ...
Neutralization Theory - Criminology - Oxford Bibliographies - obo Sykes and Matza outlined five neutralization techniques: denial of responsibility, denial of injury, denial of victims, appeal to higher loyalties, and condemnation of condemners. Research on the theory has generally produced mixed results, leading many to conclude that the theory is not powerful enough to serve as a stand-alone explanation for ...
Under what circumstances, the Puma Swaraj was demanded by the ... - Pyranic under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? by Get Answers Chief of LearnyVerse (321k points) asked in Other Sep 10, 2021. 0 votes. 89 views 1 answer. under which of the following circumstances would we observe the greatest increase in real income?
MCAT Psych/Sociology from 132 Scorer Flashcards | Quizlet Looked at the economic conflict between different social classes, and argued that societies progress through class struggle between those who own and control production and those who labor and provide the manpower for production. Believed that capitalism would ultimately lead to self-destruction of society due to internal tensions.
Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to ... The circumstance that can lead a deviant label from primary to secondary deviance is when the deviant label is applied later in life What is labelling theory? According to the labeling hypothesis, the terminology used to define or categorize people may determine or have an impact on their behavior and sense of self.
Sociology Unit 2 Flashcards | Quizlet How secondary groups lead to primary groups. ... How can deviance be explained by the functionalist perspective. through strain theory. ... Under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance? when the deviant label is accepted by the individual and seen as deviant.
Secondary Deviance: Definition & Examples - Study.com Primary deviance is a deviant act that receives little social reaction or mild, corrective reaction. It's important to remember that not all deviant acts produce long-term negative outcomes. Some...
Putting Case Studies to Work: Applications to Development Practice ... The Case for Case Studies - May 2022
Sociology Exam 2 Flashcards | Quizlet Under what circumstances does a deviant label transition from primary to secondary deviance? a.when the deviant label is internalized b.when the deviant label is applied by a large number of people c.when the deviant label is applied later in life d.when the deviant label is applied by someone very powerful a.when the deviant label is internalized



























Post a Comment for "40 under what circumstances does a deviant label lead from primary to secondary deviance?"