40 bioninja digestion
PDF Topic 2.3: CARBOHyDRATES - BioNinja Carbohydrate Lipid Storage Short term Long term Osmolality More effect Less effect Digestion Easier to digest Harder to digest ATP Yield Smaller Larger (~2×) Solubility Soluble (mono-/dimer) Insoluble in water Body Mass Index While carbohydrates (and lipids) are important components of a healthy diet, excess intake can affect body mass Gastrointestinal | Digestion & Absorption of Carbohydrates Gastrointestinal | Digestion & Absorption of Carbohydrates - YouTube Official Ninja Nerd Website: Nerds!In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be teaching you...
Stages of Digestion | BioNinja | Biology lessons, Digestion, Physiology Apr 22, 2020 - This Pin was discovered by Feast School. Discover (and save!) your own Pins on Pinterest
Bioninja digestion
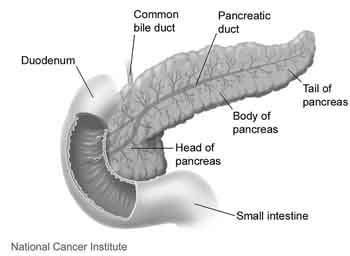
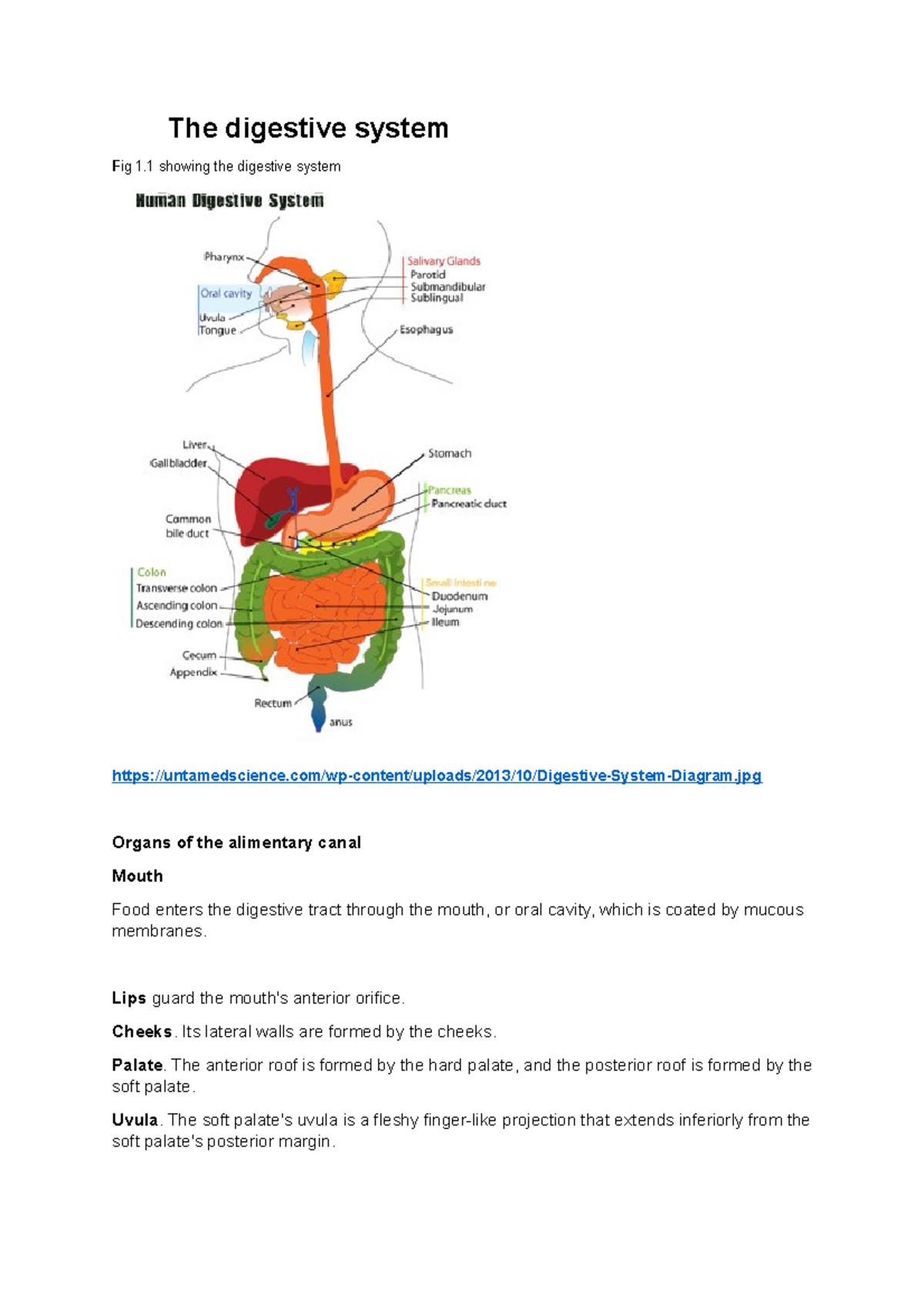
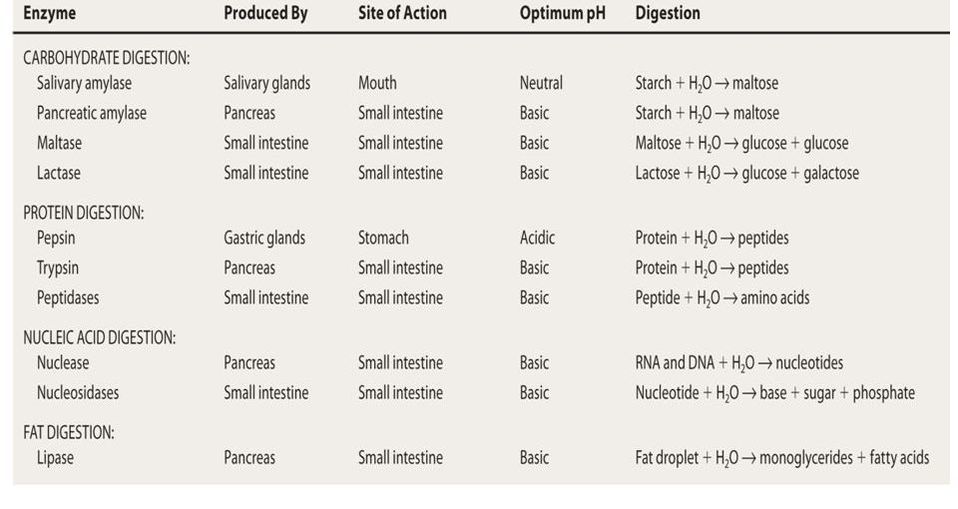
6.1 Digestion and Absorption | BioNinja Villi absorb monomers formed by digestion as well as mineral ions and vitamins; Different methods of membrane transport are required to absorb different nutrients; Applications: Processes occurring in the small intestine that result in the digestion of starch and transport of the products of digestion to the liver PDF Topic 6.1: DIGESTIOn - BioNinja The digestive system is composed of the alimentary canal and a variety of supporting accessory organs Alimentary Canal (directly transfers food) • Oesophagus - Food tract from mouth to stomach • Stomach - Storage tank with low pH (protein digestion) ... bioninja Created Date: PDF 6.1 Digestion & Absorption - BioNinja Mechanical digestion is the breakdown of food by physical action (e.g. chewing, churning, segmentation) Chemical digestion is the breakdown of food by chemical agents (e.g. stomach acids, bile, enzymes) Complete the following table Enzyme Source Substrate Product Optimal pH (salivary) amylase pepsin
Bioninja digestion. 6.1 Digestion | BioNinja H2 Digestion; H3 Absorption of Digested Foods; H4 Functions of the Liver; H5 The Transport System; H6 Gas Exchange; Additional Resources. Biology Quick Reference Guides; Biology Songs; Biology Tutorials; Biology Powerpoints; BioNinja App (beta testing) 6.1 Digestion. Previous. Next. List. 6.2, 6.2, 6.4 Bioninja Notes.pdf - 6.1 Digestive System... 6.1 Digestive System There are two major groups of organs which comprise the human digestive system: The alimentary canal consists of organs through which food actually passes (oesophagus, stomach, small & large intestine) The accessory organs aid in digestion but do not actually transfer food (salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gall bladder) Alimentary Canal: Oesophagus A hollow tube ... Subject Biology. dihybrid cross practice worksheet answer key Bing ... Download BioNinja IB and enjoy it on your iPhone, iPad, and iPod touch.Bioninja / Silver 3 61LP / 81Win 82Lose Win Rate 50% / Zyra - 24Win 12Lose Win Rate 67%, Nami - 11Win 14Lose Win Rate 44%, Janna - 14Win 10Lose Win Rate 58%, Vel'Koz - 8Win 6Lose Win …Welcome to the BioNinja VCE website - your one-stop resource for everything related to ... DigestionNotes&HW.pdf - IB Bio 2: Digestive System (using... IB Bio 2: Digestive System (using Course Companion and Bioninja) 1. Identify the correct structure and function for the diagram to the right. You will be required to reproduce something similar on an assessment! (p.280) Diagram number Structure Function 1 Salivary Gland Releases saliva to break down food and contains enzymes to initiate starch breakdown. 2 Oesophagus Connects the oral cavity ...
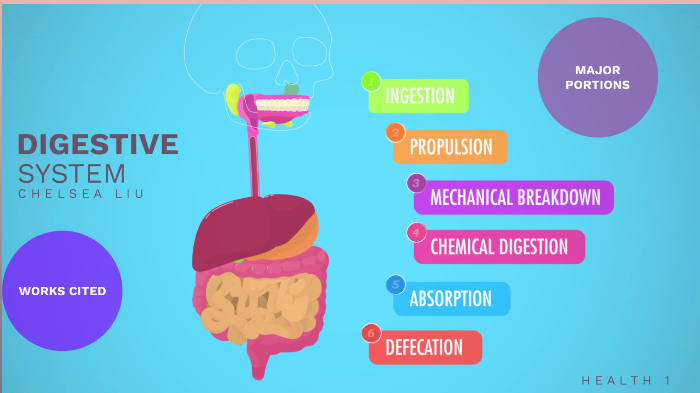
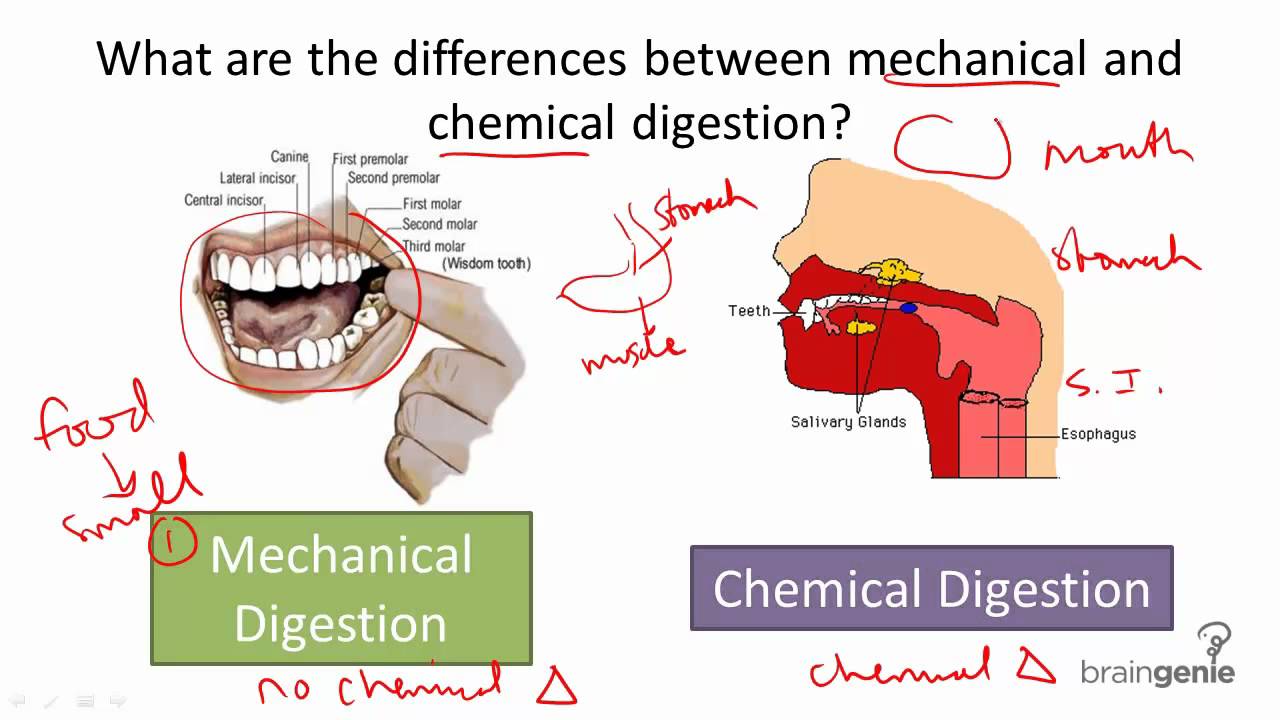
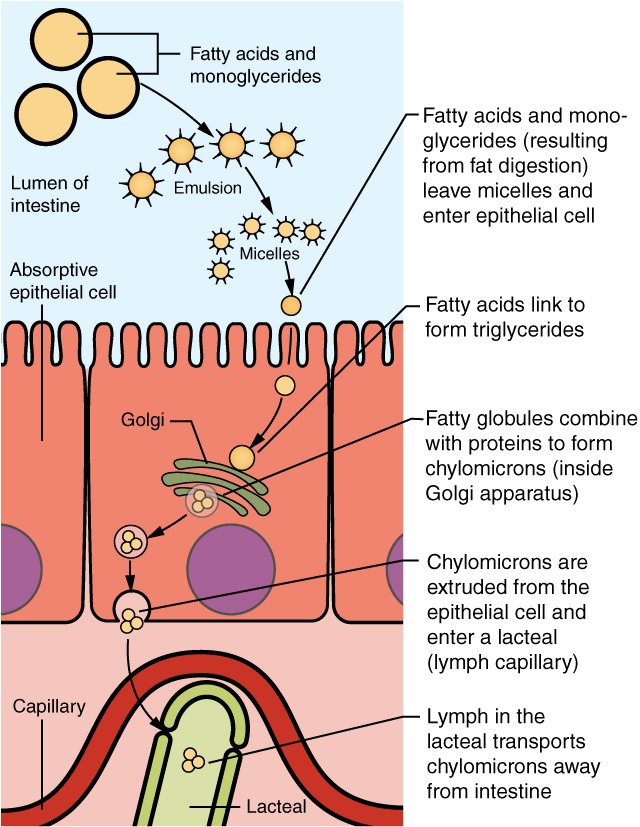
Mechanical Digestion | BioNinja The stomach lining contains muscles which physically squeeze and mix the food with strong digestive juices ('churning') Food is digested within the stomach for several hours and is turned into a creamy paste called chyme Eventually the chyme enters the small intestine (duodenum) where absorption will occur Movement of Food Peristalsis Lipid Digestion | BioNinja.pdf - HOME STANDARD LEVEL HIGHER... View Lipid Digestion | BioNinja.pdf from BIOTECH BBT098 at Harvard University. HOME STANDARD LEVEL HIGHER LEVEL OPTIONS ADDITIONAL RESOURCES Lipid Digestion Lipids are hydrophobic (water 'hating') Home Page | BioNinja 1. Metabolic Molecules 2. Water 3. Carbohydrate & Lipid 4. Protein 5. Enzymes 6. DNA / RNA Structure 7. DNA ⇒ Protein 8. Cell Respiration 9. Photosynthesis 3: Genetics 1. Genes 2. Chromosomes 3. Meiosis 4. Inheritance 5. Genetic Modification 4: Ecology 1. Species & Ecosystems 2. Energy Flow 3. Carbon Cycling 4. Climate Change 5: Evolution 1. Chemical Digestion of Carbohydrate, Protein, Lipid, Nucleic Acid The six steps of the digestive process include ingestion, propulsion, mechanical or physical digestion, chemical digestion, absorption, and excretion. Digestive enzymes are produced by the bacteria, often known as gut flora or microbiome in our GI tract. Moreover, a portion of the nervous and circulatory systems have a role, too.
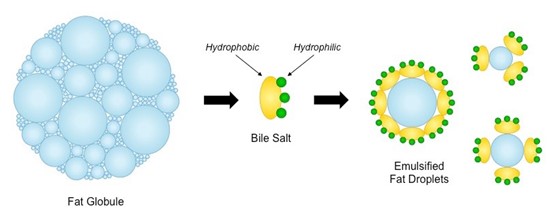
Chemical Digestion | BioNinja Food can be digested by a combination of two methods - mechanical digestion and chemical digestion In chemical digestion, food is broken down by the action of chemical agents (such as enzymes, acids and bile) Stomach Acids The stomach contains gastric glands which release digestive acids to create a low pH environment (pH ~2) Digestive System | BioNinja • A temporary storage tank where food is mixed by churning and protein digestion begins • It is lined by gastric pits that release digestive juices, which create an acidic environment (pH ~2) Small Intestine • A long, highly folded tube where usable food substances (nutrients) are absorbed Lipid Digestion | BioNinja Lipid Digestion | BioNinja Lipid Digestion Lipids are hydrophobic (water 'hating') and hence tend to be insoluble within the aqueous environments of the body Being hydrophobic, lipids will group together (coalesce) to form large globules of fats Stages of Digestion | BioNinja The process of digestion occurs across a number of stages, including: Ingestion - food is taken into the body via the act of eating Digestion - food is broken down both physically (e.g. mastication) and chemically (e.g. enzymatic hydrolysis) Absorption - digested food products are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to cells
Chemical Digestion | BioNinja | Teaching biology, Endocrine system ... Great tool for solving three simple algebraic equations essential to solution chemistry. Just cover up the variable you are solving for, and the arrangement of the other two variables shows if you should multiply or divide them to solve for your unknown. For example, multiple molarity (M) and volume (L) to solve for moles of solute in a solution.
PDF 6.1 Digestion & Absorption - BioNinja Complete the following table Enzyme Source Substrate Product Optimal pH (salivary) amylase pepsin (protease) (pancreatic) lipase Compare digestive movement via peristalsis and segmentation
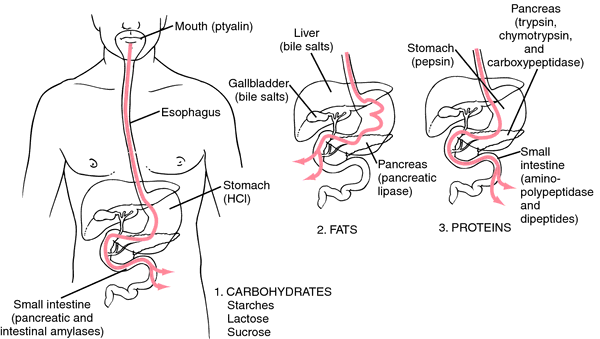
6.1 Digestion | BioNinja 6.1.4 Draw and label a diagram of the human digestive system. There are two major groups of organs that comprise the human digestive system: Alimentary Canal: Contains organs through which the food actually passes (esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, etc.) Accessory Organs: Organs that assist in digestion but no food passes ...
Modelling Digestion | BioNinja The process of digestion therefore performs two key functions: It breaks down insoluble molecules into smaller subunits which can be readily absorbed into body tissues It breaks down inert molecules into usable subunits which can be assimilated by cells and reassembled into new products Modelling Digestion
H2 Digestion | BioNinja Some digestive enzymes are immobilised on the plasma membrane of the epithelial cells of the small intestine, serving two main benefits: 1. The enzyme is fixed in place and does not pass through the digestive system, meaning it can be reused 2. The enzyme can be linked to secondary functions (e.g. membrane transport) Example:
Digestive System - BioNinja | PDF Digestive System _ BioNinja - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. human digestive system
PDF BioNinja Revision Notes Digestion (6.1) Why digestion occurs (6.1.1) • Most food is in the form of large complex molecules which are insoluble and chemically inert • Breaking food down (digestion): - Makes it soluble & able to be absorbed - Generates usable building blocks Role of enzymes (6.1.2) • Enzymes lower the activation energy for chemical reactions ...
BioNinja Digestion.docx - BIN:_ BioNinja Digestion Part 1:... BIN:_____ BioNinja Digestion Part 1: Create an annotated diagram of the digestive system. (On separate, blank white paper) Part 2: Mechanical and Chemical Digestion. Mechanical: Mechanical Digestion: Chewing (_____________) Churning (_____________) Movement of Food: Peristalsis Segmentation Chemical: Stomach Acids Bile Enzymes
PDF 6.1 Digestion & Absorption - BioNinja Mechanical digestion is the breakdown of food by physical action (e.g. chewing, churning, segmentation) Chemical digestion is the breakdown of food by chemical agents (e.g. stomach acids, bile, enzymes) Complete the following table Enzyme Source Substrate Product Optimal pH (salivary) amylase pepsin
PDF Topic 6.1: DIGESTIOn - BioNinja The digestive system is composed of the alimentary canal and a variety of supporting accessory organs Alimentary Canal (directly transfers food) • Oesophagus - Food tract from mouth to stomach • Stomach - Storage tank with low pH (protein digestion) ... bioninja Created Date:
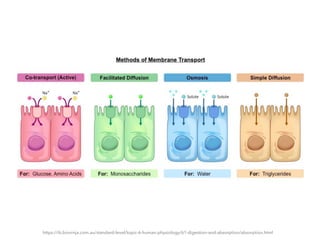
6.1 Digestion and Absorption | BioNinja Villi absorb monomers formed by digestion as well as mineral ions and vitamins; Different methods of membrane transport are required to absorb different nutrients; Applications: Processes occurring in the small intestine that result in the digestion of starch and transport of the products of digestion to the liver















Post a Comment for "40 bioninja digestion"